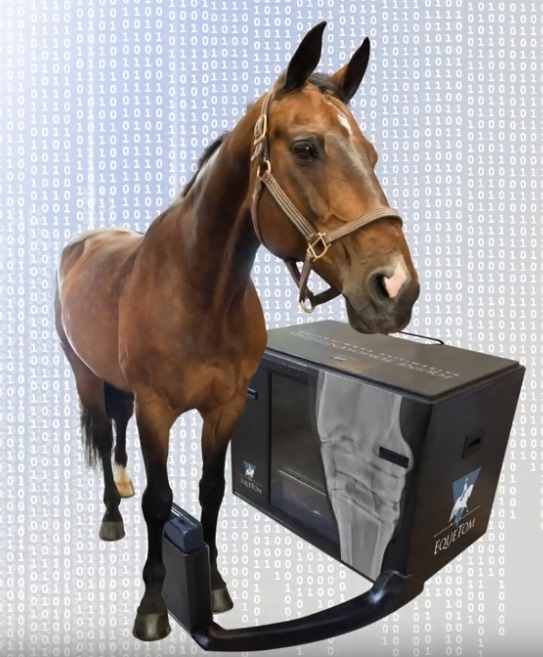
Portable tomosynthesis system for the equestrian market
To order
Digital X-ray tomosynthesis (DT) - a new method of examination in veterinary medicine. The simplicity of the survey, DT close to Digital Radiography (DR), and performance, it is close to, Computed Tomography (CT). Development of X-ray examination methods leads to an increase in the measured parameters of diagnostic images. DT provides new opportunities for consideration, and for measuring the parameters of layer images.
New tomosynthesis system for the equestrian market - a diagnostic X-ray machine in the world for the first examination of horses with the use of digital tomosynthesis. It embodies the principle - not to lead the horse to the CT, and bring CT to the horse.
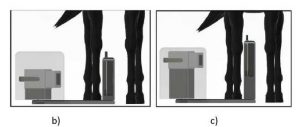
During the test, the horse stands quietly on dry hard surface, and the operator sets the ET device to the desired position (Figure b, c).
During the scanning procedure the X-ray generator moving inside ET-portal for 2,5 … 3,2 with. During the scan, a dynamic digital X-ray receiver (DDR) generates 85 … 120 X-ray images (projections) the survey of the horse, taken from different angles. The obtained X-ray images are transferred to the computer. Further conducted tomographic reconstruction and mapping of about 150 … 340 X-ray detector in parallel with the layers of plane.
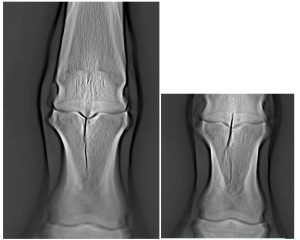
Images in cross-section tomosynthesis
In appearance, image layers in a system with tomosynthesis (DT) different from the digital X-ray images (DR) and CT-images. Consideration doctor DT-image similar to the optical image by using a microscope or binoculars. In these cases,, applied in depth focusing. In DT-recorded image clear X-ray image layer to a certain depth and attenuated Defocused images adjacent layers.
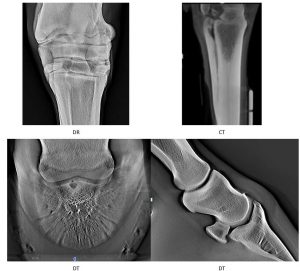
Defocused presence of adjacent layers on DT-image allows the operator to inspect the inspected object by its depth. Same, human vision in daily life. Consequently, DT-sequence image layers more accustomed, than the sequence of CT-sections. Besides, DT-image of tomosynthesis systems have about twice as many parts, compared with the traditional images of CT-scanners.
Analysis layers diagnostic sequence DT-image has great advantages, compared with the analysis of DR-images.
Image quality tomosynthesis
The doctor may look at the original X-ray image DDR, but it is much more convenient to analyze the images after tomographic reconstruction. The presence of layers tomosynthesis enables:
- Conveniently demonstrate these capabilities at example images of the phantom limb joint of a large animal. This phantom is the real bone and cartilage of the joint, and additional test facilities, simulating various types of pathologies, occurring at various injuries and diseases in the joints of horses limbs, consider examination object in a sequence of layers of images of individual parts, focused at different depths;
- Consider the details of the subject with a contrast agent is several times higher, than the contrast of the object parts in the X-ray image;
- Measure the spatial dimensions of objects without increasing the geometric errors;
- Measure the depth of a particular part of the object by the number of layers;
- Evaluate X-ray density of the object in a specific layer, taking into account the impact of the weakened defocused images of adjacent layers;
- Measuring small saturation level of structural elements in a certain layer.
During the review and measurements using the user interface, which has a main window: “Database”, “Radiografiya” and “Tomography”. These windows define the basic mode, the user works: Selection of patients and diagnosis images for, Analysis of X-ray imaging and analysis of tomosynthesis.
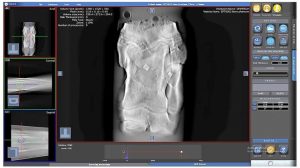
At the time of diagnosis of the new system, you can not just subjectively considered tomographic image layers, but also to carry out objective measurements. According to the results of one scan, we can estimate the size of pathologies on all three coordinates, X-ray density and its heterogeneity. The measurements provide the evidence base for diagnosis.
EXPERT OPINION: Tomosintyez, A new revolution in 3D X-ray diagnosis
PhD, licentiate in veterinary Thais Ribera. Graduate Veterinary Joana Ramos, licentiate in veterinary medicine, Master of Science, with a degree of ECVS / ACVS Miguel A. Valdez. Medical and Diagnostic Center La Ekin (Malaga), Spain.
horse tomosynthesis, It is a milestone in the path of the tomographic diagnosis of horses. This adaptation of the three-dimensional mammography (tomosinteza) of human medicine. This method complements mammography and radiography is to obtain several two-dimensional X-ray images with low radiation, parallel detector, thereby avoiding the imposition of anatomical structures and allows you to more accurately determine the three-dimensional location of the breast lesion. Our center is the first in Europe, Set this technology. We describe a comparison between conventional radiography, tomosynthesis, and in some cases, magnetic resonance imaging (MRT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Technics: TSE performed with the horse in the season and under sedation. It consists of a light box poluportativnogo (1,20x70x60 cm) weight 48 kg X-ray generator, which moves on motorized rail. performed 339 radiographic projections for 5 seconds, while the generator is moving horizontally at a constant speed rail, rotating an arc of 20º. A set of images captured by the high-speed data transmission tomography detector and restored on a computer with software, which restores 339 slice thickness monoplanar 1,6 mm each. Generator and detector system and fixed arc magnetization support (drawing 1).
Studied three-dimensional anatomical structures observed during the passage of successive slices. The overlap is kept to a minimum and allows a consistent approach to the various anatomical structures, that facilitates the spatial arrangement and diagnostic interpretation defeats, give the perception of a three-dimensional pattern.
the, that can be explored, is the head (to 44 cm width) and all of the distal region of the extremities of the tibia and distal radius. possible projection: lateralyno-lateralynaya (L-L) head; lateral-medial standard (LM) or flexion (flexion LM), dorsoladonnaya / plantar (DP) and oblique (dorsomedial-palmar / plantar and palmar-dorsolateral / medial plantar) limbs in addition to the DP 45º hoof (navicular bone and the third phalanx), Using podoblok to place the hoof. For this latter projection is desirable to remove a shoe sole and a good clean, to minimize possible interference by it or gravel, who could stay, and the optimum quality of the image and the correct interpretation radiological.
For the study of the head in the system has a hydraulic table, which allows the car to raise the height of a horse's head. In these cases, in order to minimize the interference due to the presence of metal in usual bridles, worn rope bridle.
RESULTS
collected stories 35 observations, made in the last 3 of the month. The horses were of different breeds (polo, Spanish sports horse, Andalusian horse, Central European, Anglo-Arabian horses), birth, fitness (polo, for show jumping, dressage, morphological, pleasure) and ages (from 1 weeks of life until 27 years old). There were studied 4 head, 2 wrist, 4 instep bone, 6 fetlock, 6 metacarpals and 8 hoof. In all cases, X-ray study was carried out with a wireless DR, and 4/8 cases with pathology in the hoof is supported by research into MRI.
The average duration of the studies was approximately 15 minutes on the area, it usually was done by one or two areas on the horse. The average duration of the exam was the head 10 minutes.
None of the 35 studies was not a single incident or management problems. Diagnosed following pathologies: tooth root infection, cementoma (head); osteoarthritis (OA) in various joints; sagittal fracture of the first phalanx, degeneration in bone chelnochnoy, navicular bone avulsion at the beginning of the unpaired ligament, gap in the navicular bone in the beginning of the unpaired ligament, osteitis in the third phalanx, focal mineralization internal finger-flexor tendon, osteochondrosis dissecans osteocondritis dissecans (OCD) difficult to interpret for radiography, chronic fracture of the talus, fracture of the third metatarsal bone exostosis, and the 2nd and 4th metacarpal / metatarsal bone and osteochondral fragmentation (fracture "chip"). IN 4 horses, we were able to complement the study of MRI, that helped confirm the results obtained in X-ray and diagnostic TSE TSE superiority compared to classic digital radiography.
In all clinical observations TSE added some radiological findings, representing the clinical or surgical interest, no appreciable or questionable for classical radiography. At the end of trial, usually, needed only two projections (LM и DP). However, in some specific cases, such as pathology rudiments, It is also recommended to perform both oblique projection. It is impossible to make a projection proksimodistalnuyu (skyline). Also not available proximal anatomical areas, such as knees, neck, back or pelvis.
Interference, caused by the presence of screws, bandage or fiberglass, It is not a limiting factor for the radiological assessment. The TSE structures do not overlap each other, that allows us to investigate topographically each anatomical structure in the context of non-overlap. Because of this, the image quality and diagnostic accuracy of the above, in comparison with the direct digital radiography. AT 4 of 8 cases with pathology of the hoof, in which we were able to complement the study of MRI, It confirmed, that radiological signs, observed only in TSE, confirmed.
DISCUSSION / CONCLUSION
TSE involves a new technique tomographic diagnosis, complementary digital radiography, and functions, which hitherto could only be achieved using Computed Axial Tomography (CT) or MRT. This allows you to quickly and under sedation to obtain a set of serial radiographic images, which after renovation can avoid bone overlap of various anatomical structures in the same plane and allow details to determine the location, and at the same time to obtain a spatial vision of the specific lesions, increasing thereby the accuracy of diagnosis, together with clinical parameters.
TSE poluperenosnym is suitable for transportation and, It has conveyed to the size of a pickup truck (Picture 1). Its use is practical and fast, and until now there were no incidents registered with horses. Interpretation of the images as a whole does not need any help from the outside of specialized personnel and needs a very brief period of training. It is much cheaper tool, than CT, which can be used immediately in the same facilities, where the patient, and its acquisition does not involve additional costs for consumables or special maintenance.
Radiation, emitted at each irradiation, More logically, than from conventional digital radiography, but also a lot less, than emitted during CT. Radiation, staff received, much less, than is obtained when a patient, because a powerful magnet, which holds the detector, It allows, so that no one held it while taking pictures (Picture 1). Dosimeter readings of our staff did not record increase.
TSE does not intend to replace digital radiography, but to improve its diagnostic possibilities in cases, when the results of radiological investigations do not allow definitive conclusions. This method is particularly recommended to obtain more accurate diagnosis of pathologies head, such as alveolar lesions sinus infection, fractures of the lower / upper jaw or frontal / nasal bone, pathologies of the distal finger (podotrohleit or navicular syndrome, especially the navicular bone and the third phalanx). This is particularly informative when determining the fracture configuration without displacement, position in a joint-free chips or adhering to the capsule, articular space in three-dimensional perception and evaluation of the gap between the cortical bone and the fragments in case exostosis and sequesters.
CONCLUSION / CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
TSE – It is a powerful tool tomographic diagnosis, complementary digital radiography, with limbs and head, which allows to obtain three-dimensional information, which until now offered only CT. The ability to perform this test «in situ», in other hospitals, horse and competitive areas, at the station under sedation and immediate form, It is making it a very useful tool for radiological diagnostics for field clinics, providing information so far exclusive to other more advanced and less affordable methods.
LIST OF REFERENCES
- The first portable tomosynthesis system for equine market. lusoelectronics.com> Brochure_ET_Luso Services and Rimtech, 2019. EqueTom Brochure.(pdf)
- Equetom-Portable Equine Tomosynthesis System. veterinary-imaging.com. Universal Medical Systems. 2019
- Arlette Perez Elizalde. breast tomosynthesis: physical bases, indications and results. Department of Radiology, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain. Vol.28. n.1, pp39-45,
Picture 1: (left) Patient during the inspection of the site and interphalangeal hoof left thoracic limb lateromedialnoy projection. note: arc detector keeps, thereby removing the need for, Assistant to the detector held in the desired position. (case) Tomosynthesis apparatus during transportation in an ordinary passenger car.
Picture 2: cementoma shot at the root of the left first molar. Right cut two sagittal fracture of the proximal phalanx without bias. The cut slice of the middle zone and the dorsal zone. This makes it possible to reconstruct the dorsomedial helicity fracture.